Why Did Mortgage Rates Rise After the Fed Cut Interest Rates?
On September 18, the Federal Reserve surprised the market by cutting interest rates by 50 basis points, kicking off a new loosening cycle to ease financial conditions. Typically, when the Fed cuts rates, we expect borrowing costs, including mortgage rates, to decrease. However, in an unexpected turn, average 30-year mortgage rates actually rose by 50 basis points, bringing them to around 6.60%. So, what’s causing mortgage rates to move in the opposite direction?

Strong Jobs Growth and Hotter-Than-Expected Inflation
The answer lies in the latest economic data, particularly around jobs and inflation. Just days after the Fed’s rate cut, the September jobs report showed stronger-than-expected employment growth, a clear indicator that the economy is still running hot. When the job market is this strong, it can signal rising wages and increased consumer spending, which often puts upward pressure on inflation.
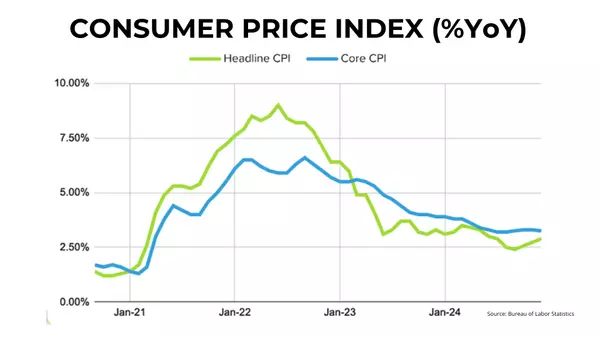
Speaking of inflation, the latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) numbers from September weren’t as favorable as markets had hoped. While the headline CPI (which measures overall inflation) eased slightly to +2.4% year-over-year, down from +2.5% in August, the core CPI (which excludes volatile food and energy prices) actually ticked up to +3.3% YoY, from +3.2% in the previous month. Both of these figures came in higher than economists expected, signaling that inflationary pressures are still present.
Why Did Mortgage Rates Rise?
You might wonder, why would mortgage rates climb when the Fed is cutting rates to stimulate the economy? It’s because mortgage rates are more directly tied to long-term economic expectations rather than the short-term actions of the Fed. When inflation is expected to stick around, even at slightly elevated levels, lenders will price that into their long-term loans, which includes 30-year mortgages. Add to that a strong labor market fueling economic activity, and you’ve got conditions that push mortgage rates higher.
In simple terms, while the Fed is doing its part to loosen financial conditions, strong jobs growth and persistent inflation are keeping mortgage rates elevated, at least for now.
What’s Next for Mortgage Rates?
While this latest economic data isn’t a cause for alarm, it has certainly created uncertainty in the housing market. If inflation and job growth continue to run hotter than expected, mortgage rates could stay higher for longer, despite the Fed’s efforts to cool things down. On the flip side, if we start to see inflation ease and job growth moderate in the coming months, we could finally see mortgage rates respond by heading lower.
For now, though, anyone in the market to buy or sell a home needs to keep a close eye on these economic trends. The interplay between inflation, jobs, and Fed policy will continue to shape the housing market as we move further into 2024.
Conclusion
In the real estate world, it’s never just about one factor. While the Fed’s rate cut signaled an easing stance, the broader economic picture—particularly stronger jobs growth and stubborn inflation—is what’s driving mortgage rates higher.
As a result, buyers and sellers should prepare for potential rate volatility as the market continues to adjust to these conditions.
If you’re thinking about buying or selling a home in this evolving market, it’s essential to stay informed and work with a knowledgeable real estate professional who can help you navigate these changing dynamics.
Categories
Recent Posts







GET MORE INFORMATION

